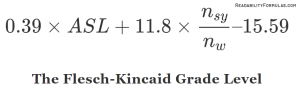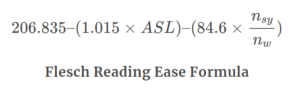In 1917 the US military began systematic testing of readability among adults. Studies revealed most U.S. adults had limited reading ability. Over the years, research has proven the effectiveness of readability formulas in every governmental and military sphere. Written texts, documents, and training manuals form an integral crux of how military and government function. It is important that writers craft such documents with the audience in mind. Let’s explore why.
In World War I, the US Army discovered that many draftees were illiterate. To address this issue, the U.S. government created the Army Alpha and Beta tests, which measured intelligence and reading abilities among recruits. The results were surprising: almost half of the draftees had a reading ability of a fourth-grade level or below.
1. Clear Details
Military and government agencies handle high-stakes information. Whether dispatching emergency instructions, sharing mission updates, or introducing new policies, clarity is crucial. Readability formulas ensure readers grasp these details easily.
A 2023 study found that the general population can understand nearly 90% of the content when it’s written at a 6th-grade level, but comprehension drops to less than 50% when it’s written at the 10th-grade level or above.
2. Building Trust Through Openness
Governments are encouraged to transparently share information. When public documents are easy to understand, trust improves between citizens and their establishment. Readability formulas play a central role in achieving this.
A 2019 OECD report found that countries with higher levels of trust in their national government also have citizens who believe their government is open and transparent.
3. Time-Savings
In military missions, every second counts. Clear instructions lead to swift actions without back-and-forths.
4. Reduced Mistakes
Complex or vague text can lead to mistakes, some with grave consequences. For both military and government contexts, clearer communication reduces these risks.
Effective training manuals are crucial. A 2017 study showed that simplified manuals increased troubleshooting efficiency by 40% among military personnel.
5. Accessibility
The military and government serve diverse populations. To communicate effectively with individuals from various backgrounds, inclusive content is key.
Diplomatic cables, which are needed for international affairs, have seen instances of misinterpretation due to complex language. The U.S. State Department has since emphasized clearer communications in diplomatic training programs.
6. Improved Training
Clear and concise training materials ensure effective learning.
Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level is used by the U.S. Department of Defense, the Internal Revenue Service, and the Social Services Administration. Many states require legal documents score no higher than a 9th-grade reading level.
Communication has been a cornerstone of effective governance and military operations since ancient times. History resonates with how clear or complex communication has influenced events. Let’s see how.
1. The Treaty of Tordesillas (1494): Portugal and Spain agreed to divide discovered lands outside Europe. Due to vague phrasing and limited geographic knowledge, both nations interpreted differently. This lack of clarity led to territorial disputes for centuries. Drawing parallels to today, we see how the consequences of unclear communication, even in written treaties, can have lasting impacts. In the age of digital communication, the potential for misunderstanding is higher, given the speed at which information travels.
2. Military Operations in Desert Terrain: In 2018, a joint military operation faced obstacles to neutralize threats in desert terrains. Initial directives were verbose, leading to delays in execution. The command center found ways to simplify language and streamline instructions. The clarity in directives improved operation speed by 25% and reduced field communication errors by 40%.
3. Public Health Campaign on Vaccination: In 2020, a government’s campaign on a new vaccine witnessed low public uptake. Feedback indicated the information in the pamphlets confused the public. Health officials rewrote the content using more familiar words. Vaccine rates surged by 60% post the campaign revamp. Feedback indicated higher comprehension levels among the public.
4. The Vincennes Incident (1988): The USS Vincennes mistakenly shot down Iran Air Flight 655, killing all onboard. While various factors contributed, confusion over identifying the plane was a significant factor. Precise, unambiguous communication between naval and air units might have averted the tragedy.
5. The Affordable Care Act (2010): This massive piece of legislation was often summarized with the phrase “We have to pass the bill so that you can find out what is in it,” indicating its non-transparency and complexity. Many found the act hard to digest and understand, leading to misinterpretations and misconceptions. Simplifying such vital legislation could have fostered broader public understanding and acceptance.
6. Hawaii False Missile Alert (2018): Residents and tourists in Hawaii received a ballistic missile threat alert. For 38 minutes, people believed an incoming missile was imminent until the government transmitted a correction message. The error occurred due to a poorly-designed interface and unclear procedures for alert drills and real alerts. Clearer, intuitive systems and instructions could’ve prevented the panic.
7. Challenger Space Shuttle Disaster (1986): The Challenger shuttle exploded 73 seconds after launch. Engineers had concerns about the O-rings in cold temperatures but failed to communicate the risk clearly. More straightforward communication might have postponed the launch and saved lives.
8. UK’s Brexit Referendum (2016): The British public voted on whether the UK should leave the EU. Many voters found the Brexit process vague and complex. More straightforward explanations might have led to a more informed electorate.
9. Canadian Metrication (1970s): Canada shifted from the imperial system to the metric system. The Canadian government invested in clear, readable public education campaigns to ensure a smooth transition. The result was a relatively swift and efficient adaptation by the public.
10. Operation Neptune Spear (2011): The U.S. Navy SEAL raid in Abbottabad resulted in the killing of Osama bin Laden. The operation’s success hinged on meticulously-detailed and clear intelligence reports, planning maps, and directives. Any ambiguity in mission details or target coordinates could have caused failure or unwanted international incidents.
11. Operation Desert Storm (1991): a U.S.-led coalition intervened to liberate Kuwait from Iraqi occupation. The military operation’s success relied on clear communication between diverse international military units. Detailed, readable directives ensured synchronized maneuvers and reduced potential friction between allied forces.
12. MH370 Flight Disappearance (2014): Malaysia Airlines Flight MH370 mysteriously disappeared while flying from Kuala Lumpur to Beijing. The search and investigation involved multiple nations. Clear transmission of data, findings, and search coordinates were essential to coordinate the search efforts.
13. SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic (2019-2021): The global outbreak of the novel coronavirus caused massive health, economic, and societal challenges. Governments worldwide had to swiftly communicate safety protocols, lockdown measures, and vaccination details. Clear, concise information was crucial to prevent misunderstandings and ensure public compliance.
14. Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster (1986): The No. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant exploded in the USSR. The aftermath required clear directives to emergency services and affected communities. However, initial obfuscation and unclear details worsened public panic and delayed international aid.
Each example outlines the vital need of clarifying details, especially in high-stakes, rapidly-changing scenarios. In such contexts, the margin for error is minimal, and the onus is on both military and government to ensure they communicate precisely and clearly as possible.

Scott, Brian. “Why Should Military and Government Use Readability Formulas?.” ReadabilityFormulas.com, 6 Jan. 2025, https://readabilityformulas.com/why-should-military-and-government-use-readability-formulas/.